South China Sea dispute: Why can't Southeast Asian countries stand united against China's claims?
Amid the spectre of China's growing assertiveness in the South China Sea, Indonesia plans to convene a meeting with some of its ASEAN colleagues - including the Philippines, Vietnam and Singapore. If the meeting happens, Beijing may not dial down its activities in the disputed areas, but the point would have been made that Indonesia is prepared to take the lead in galvanising ASEAN on South China Sea matters. The idea of a meeting is not new, but this time it might just work.

Last month, the Indonesian media reported an intriguing development: the head of the country's maritime security agency (known as Bakamla), Vice Admiral Aan Kurnia, had invited his counterparts from Brunei, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Vietnam to a meeting in February to discuss the South China Sea dispute.
According to Vice Admiral Aan, the meeting would enable officials from the six countries to "share experiences and foster brotherhood" and "present a coordinated approach" so as to "respond in the field when we face the same 'disturbance'". Although he did not mention China by name, it was clear from recent events in Indonesia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) who he thought was causing the disturbance.
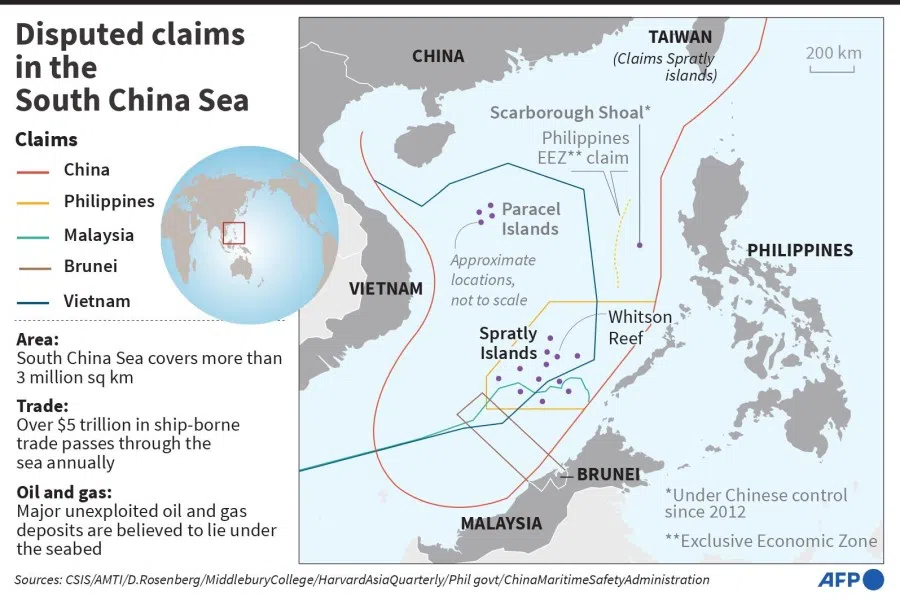
Admiral Aan's invitee list is spot on. Three of the invitees, Malaysia, the Philippines and Vietnam, occupy a number of atolls in the disputed Spratlys Islands. Brunei has never formally claimed two features which lie inside its EEZ, but China's nine-dash line skirts uncomfortably close to the country's coastline. Indonesia is a party to the dispute because China's controversial nine-dash line overlaps with its EEZ. Singapore is not a claimant but presumably was invited because as a major transhipment hub it has a vested interest in stability in the South China Sea and the free flow of maritime trade.
Vice Admiral Aan's proposed meeting has an impeccable logic to it and many would argue that it is long overdue.
The five Southeast Asian parties to the dispute have been increasingly subjected to China's "grey zone" tactics in the South China Sea. Beijing has repeatedly violated their sovereign rights by sending hundreds of fishing boats, survey vessels and drilling rigs into their EEZs, often escorted by its coast guard or navy. A discussion on how regional coast guards can effectively respond to these grey zone tactics would be very useful.
But we have been here before, and the last attempt to bring the claimant states together had mixed results.
In 2014, the Philippines - which at that time was legally challenging the nine-dash line at the Permanent Court of Arbitration - called a meeting of the four claimants. At the last moment, Brunei got cold feet and did not turn up. It is unclear what the other three countries discussed, but they never again met as a group.
Given that the Southeast Asian claimants face the same problem, why has cooperation and coordination among them been so difficult?
There are three main reasons.
In the Spratlys, Vietnam claims all of the islets occupied by Malaysia and the Philippines, while those two countries also claim each other's atolls.

The first is the problem of overlapping territorial claims and unresolved maritime boundaries. In the Spratlys, Vietnam claims all of the islets occupied by Malaysia and the Philippines, while those two countries also claim each other's atolls. And although some progress has been made in recent years, Southeast Asian governments have yet to delimit overlapping EEZs. Friction between and among them is not as intense as it was during the 1990s, but it is still an obstacle to cooperation.
The second issue is that the Southeast Asian claimants have adopted differing approaches towards the dispute. Vietnam takes a harder line against China and has demonstrated the political will to push back when necessary. The Philippines has flip-flopped between standing up to Beijing (Presidents Ramos and Benigno Aquino) and trying to appease it (Presidents Arroyo and Duterte). Malaysia downplays the dispute. Brunei mostly keeps schtum.
The third reason is a shared concern that any attempt at coordination would provoke a backlash from China. Beijing does not like the idea of the claimants discussing the dispute among themselves and presenting a common stand. It prefers a divide-and-rule, bilateral talks approach.

So what has changed since the last time a meeting of the claimants was called?
As mentioned earlier, one factor is that all of them are now under greater pressure from China to recognise its expansive nine-dash line claims. Perhaps more importantly, it might be an indication that Jakarta may finally be ready to throw overboard the fiction that it is not a party to the wider geopolitical dispute in the South China Sea. Currently, it narrowly frames the spat with China as an illegal fishing dispute.
A united front in opposition to China's claims would provoke a shrill response from Beijing. But talks on improving maritime domain awareness, sharing best practices and even pooling intelligence might be possible.
But Aan's proposal raises some interesting questions.
First, who will accept his invitation? As Bakamla's Southeast Asian counterparts are mainly civilian maritime law enforcement agencies (except for Brunei where the navy is responsible for security outside the country's territorial waters), a meeting of civilian coast guard chiefs would be less sensitive than military officers or senior diplomats. But as Singapore is not a claimant, it may stay away. Brunei's feet may still be frigid.
Second, if they do meet, what will they discuss? A united front in opposition to China's claims would provoke a shrill response from Beijing. But talks on improving maritime domain awareness, sharing best practices and even pooling intelligence might be possible.

How might China respond?
If the invitees do not RSVP that would be a win for China which might then double down on its divide-and-rule strategy.
If it goes ahead, China is likely to fume but it will not stall talks on the Code of Conduct because it wants to get it signed this year. But nor is it likely to dial down its assertive activities in Southeast Asia's EEZs.
At the very least, China will have to sit up and take note that Indonesia is discomfited with its behaviour and is willing to take the lead in pushing for a more coordinated response among the Southeast Asian claimants. That in itself would be a positive outcome of Vice Admiral Aan's maritime chinwag.
This article was first published by ISEAS - Yusof Ishak Institute as a Fulcrum commentary.
Related: Indonesia's response to China's incursions in North Natuna Sea unsatisfactory: Indonesian academic | Strong civilian presence needed to protect Indonesia's sovereignty in the North Natuna Sea | Indonesia crosses swords with China over South China Sea: 'Bombshell to stop China's expansionism'? | Indonesia-US Maritime Training Centre: A sign of Indonesia's independent and active foreign policy | Stuck in second gear: Indonesia's strategic dilemma in the Indo-Pacific





